Juvenile Pubic Symphysiodesis
Juvenile Pubic Symphysiodesis (JPS) is a straightforward procedure designed to prevent the development of osteoarthritis and hip dysplasia. It is most effective when performed on dogs between 14-18 weeks old, serving as an early intervention to potentially save on future costs and reduce the likelihood of needing additional surgery.
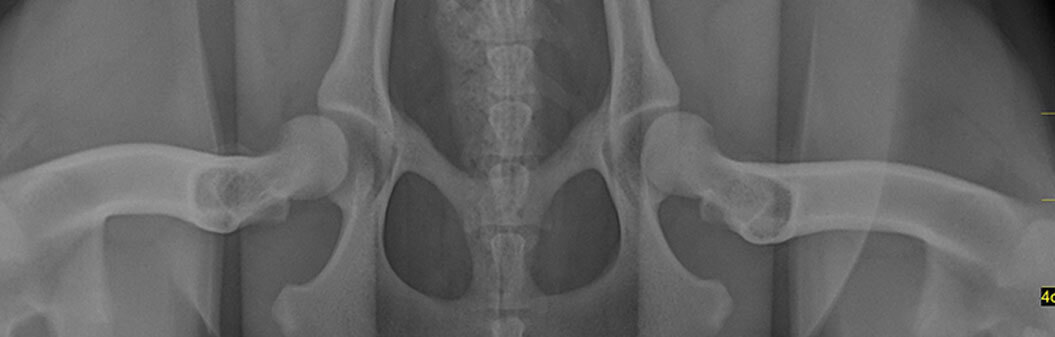
The benefits of JPS diminish significantly after 20 weeks. Therefore, we recommend conducting a PennHIP screening around 16 weeks of age. If the results show high hip laxity or a risk of hip dysplasia, JPS should be performed promptly to achieve the best outcomes.
How Is JPS Carried Out?
Juvenile Pubic Symphysiodesis (JPS) uses an electroscalpel to adjust bone development and improve hip joint coverage by closing the growth plate at the base of the pelvis. This encourages proper growth of the pelvis and hip cup, reducing hip laxity and promoting healthy hips as puppies grow.
How Do I Help My Pet Recover After Surgery?
Maintain a healthy diet and manage your puppy’s weight. For 4-6 months post-surgery, allow only leash walks and avoid strenuous exercise until follow-up exams confirm recovery. Follow-up X-rays will monitor progress, with the all-clear typically given around 10 months. About 90% of dogs benefit from this procedure, avoiding arthritis or advanced hip surgery. Puppies over 9 months may require total hip replacement as a preventative measure.
PreventHip Dysplasia
Reduces FutureSurgery Risks
ImproveLong-Term Mobility